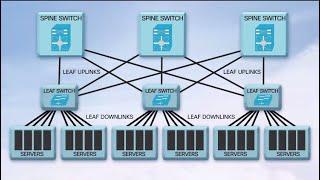
In the history of enterprise storage there has been a trend to move from local storage to centralized, networked storage. Customers found that networked storage provided higher utilization, centralized and hence cheaper management, easier failover, and simplified data protection, which has driven the move to FC-SAN, iSCSI, NAS and object storage.
Recently, distributed storage has become more popular where storage lives in multiple locations but can still be shared. Advantages of distributed storage include the ability to scale-up performance and capacity simultaneously and, in the hyperconverged use case, to use each node (server) for both compute and storage. This presentation covers:
- Pros and cons of centralized vs. distributed storage
- Typical use cases for centralized and distributed storage
- How distributed works for SAN, NAS, parallel file systems, and object storage
- How hyperconverged has introduced a new way of consuming storage
Presented by J Metz, Cisco; John Kim, Mellanox; Alex McDonald, NetApp
Recently, distributed storage has become more popular where storage lives in multiple locations but can still be shared. Advantages of distributed storage include the ability to scale-up performance and capacity simultaneously and, in the hyperconverged use case, to use each node (server) for both compute and storage. This presentation covers:
- Pros and cons of centralized vs. distributed storage
- Typical use cases for centralized and distributed storage
- How distributed works for SAN, NAS, parallel file systems, and object storage
- How hyperconverged has introduced a new way of consuming storage
Presented by J Metz, Cisco; John Kim, Mellanox; Alex McDonald, NetApp
- Category
- Network Storage
Be the first to comment