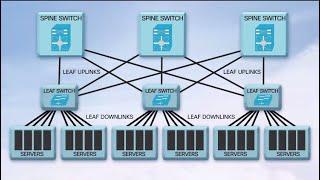
Fibre Channel, or FC, is a high-speed network technology (commonly running at 2-, 4-, 8- and 16-gigabit per second rates) primarily used to connect computer data storage. Fibre Channel is standardized in the T11 Technical Committee of the International Committee for Information Technology Standards (INCITS), an American National Standards Institute (ANSI)-accredited standards committee. Fibre Channel was primarily used in supercomputers, but has become a common connection type for storage area networks (SAN) in enterprise storage. Despite its name, Fibre Channel signaling can run on an electrical interface in addition to fiber-optic cables.
Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP) is a transport protocol (similar to TCP used in IP networks) that predominantly transports SCSI commands over Fibre Channel networks.
This video is targeted to blind users.
Attribution:
Article text available under CC-BY-SA
Creative Commons image source in video
Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP) is a transport protocol (similar to TCP used in IP networks) that predominantly transports SCSI commands over Fibre Channel networks.
This video is targeted to blind users.
Attribution:
Article text available under CC-BY-SA
Creative Commons image source in video
- Category
- Host Bus Adapters
Be the first to comment