Speakers:
Ahmed Abeer, Cisco
Neeraj Malhotra, Cisco
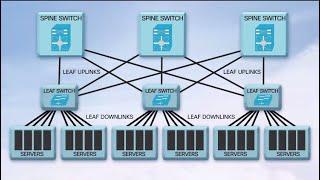
EVPN-IRB (Integrated Routing and Bridging) is a technology that leverages BGP EVPN as common overlay control plane to enable VPN routing and bridging service over an MPLS or IP underlay fabric. Point to multi-point bridging service enables VLANs to be stretched across data center IP or MPLS fabric, while VPN routing service enables inter-subnet routing across these stretched subnets. It hence allows for flexible workloads with seamless VM mobility across the stretched subnet. When designing a multi-tenant data center overlay solution using BGP EVPN control plane, multiple design options exist with respect to supporting this IRB service in the overlay: o Symmetric EVPN-IRB: with distributed first-hop any-cast GW on the ToRs o Asymmetric EVPN-IRB: with distributed first-hop any-cast GW on the ToRs o Centralized EVPN-IRB: with centralized first-hop any-cast GW on the border leafs OR DCI / DC Edge routers This talk will go over key architectural aspects that differentiate each of the above EVPN-IRB designs and focus in-depth on Symmetric EVPN-IRB design. For symmetric EVPN-IRB design, it will cover: o Overlay network architecture with respect to distributed any-cast GW and Multi-homing using EVPN-LAG o Relevant EVPN control plane constructs for IP+MAC reachability, fast convergence, BUM traffic forwarding with Designated Forwarder (DF) election and Split Horizon Group (SHG) filtering o End to End packet walk-thrus for intra-subnet bridged BUM and known unicast traffic o End to End packet walk-thrus for inter-subnet routed unicast traffic, including ARP resolution across distributed any-cast GW. o VM Mobility Neeraj Malhotra Principal Engineer, Cisco nmalhotr@cisco.com Ahmed Abeer Technical Marketing Engineer, Cisco aabeer@cisco.com
Ahmed Abeer, Cisco
Neeraj Malhotra, Cisco
EVPN-IRB (Integrated Routing and Bridging) is a technology that leverages BGP EVPN as common overlay control plane to enable VPN routing and bridging service over an MPLS or IP underlay fabric. Point to multi-point bridging service enables VLANs to be stretched across data center IP or MPLS fabric, while VPN routing service enables inter-subnet routing across these stretched subnets. It hence allows for flexible workloads with seamless VM mobility across the stretched subnet. When designing a multi-tenant data center overlay solution using BGP EVPN control plane, multiple design options exist with respect to supporting this IRB service in the overlay: o Symmetric EVPN-IRB: with distributed first-hop any-cast GW on the ToRs o Asymmetric EVPN-IRB: with distributed first-hop any-cast GW on the ToRs o Centralized EVPN-IRB: with centralized first-hop any-cast GW on the border leafs OR DCI / DC Edge routers This talk will go over key architectural aspects that differentiate each of the above EVPN-IRB designs and focus in-depth on Symmetric EVPN-IRB design. For symmetric EVPN-IRB design, it will cover: o Overlay network architecture with respect to distributed any-cast GW and Multi-homing using EVPN-LAG o Relevant EVPN control plane constructs for IP+MAC reachability, fast convergence, BUM traffic forwarding with Designated Forwarder (DF) election and Split Horizon Group (SHG) filtering o End to End packet walk-thrus for intra-subnet bridged BUM and known unicast traffic o End to End packet walk-thrus for inter-subnet routed unicast traffic, including ARP resolution across distributed any-cast GW. o VM Mobility Neeraj Malhotra Principal Engineer, Cisco nmalhotr@cisco.com Ahmed Abeer Technical Marketing Engineer, Cisco aabeer@cisco.com
- Category
- Data Centers
Be the first to comment