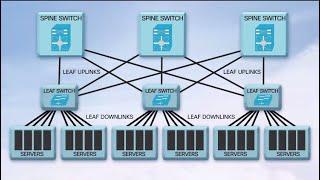
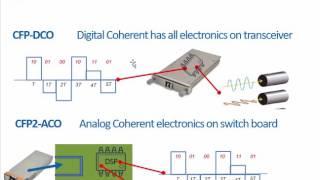
Distributed storage schemes for data centers and peer-to- peer networks often use traditional erasure codes to introduce redundancy for robustness. We will show how network coding can surprisingly reduce the communication required to maintain a storage system compared to standard Reed- Solomon codes used in current architectures. We will present both information theoretic performance bounds and achievable schemes based on novel network codes. Finally, following (very) recent developments, we will show that interference alignment is fundamental for distributed storage problems and demonstrate equivalence to a low-rank matrix completion problem over a finite field. On-going work involves the repair of existing codes used in RAID systems (like EVENODD and B-Code) and the applicability to distributed caching over mobile devices for content sharing.
- Category
- Network Storage
Be the first to comment